Propane tanks come in various sizes ranging from small 20-pound cylinders to massive storage containers exceeding 1,000 gallons. For residential and commercial applications, the most common propane tank sizes fall between 50 to 500 gallons, with the 100-gallon, 250-gallon, and 500-gallon tanks being the most popular choices for homeowners.
The right propane tank size depends on your specific energy needs, appliance requirements, climate conditions, and available space for installation. A properly sized tank ensures efficient propane delivery, reduces the frequency of refills, and provides adequate fuel supply during peak demand periods.
Key Takeaways
- The most common residential sizes are 100-gallon, 250-gallon, and 500-gallon tanks
- Tank selection should consider BTU requirements of appliances, climate, and usage patterns
- Above-ground and underground installation options are available for most tank sizes
- Proper placement and safety clearances are essential for all propane tank installations
- Larger tanks provide longer intervals between refills but require more space and higher initial investment
Why Propane Tank Size Matter?
When we talk about propane tank sizes, we’re typically referring to the capacity in gallons of propane the tank can hold. It’s important to note that propane tanks are filled to about 80% of their total capacity to allow for expansion of the liquid propane with temperature changes. This safety measure means a 500-gallon tank will hold approximately 400 gallons of propane when filled to the maximum safe level.
Propane tanks are measured in two ways: water capacity and propane tank capacity. Water capacity refers to the total volume of the tank if filled completely with water, while propane capacity is the actual amount of propane that can be safely stored (typically 80% of water capacity).
For residential and commercial use, propane tanks are available in both above-ground and underground configurations. Underground tanks offer aesthetic advantages as they’re hidden from view, but they typically cost more to install. Above-ground tanks are more affordable and easier to access for maintenance and inspections.
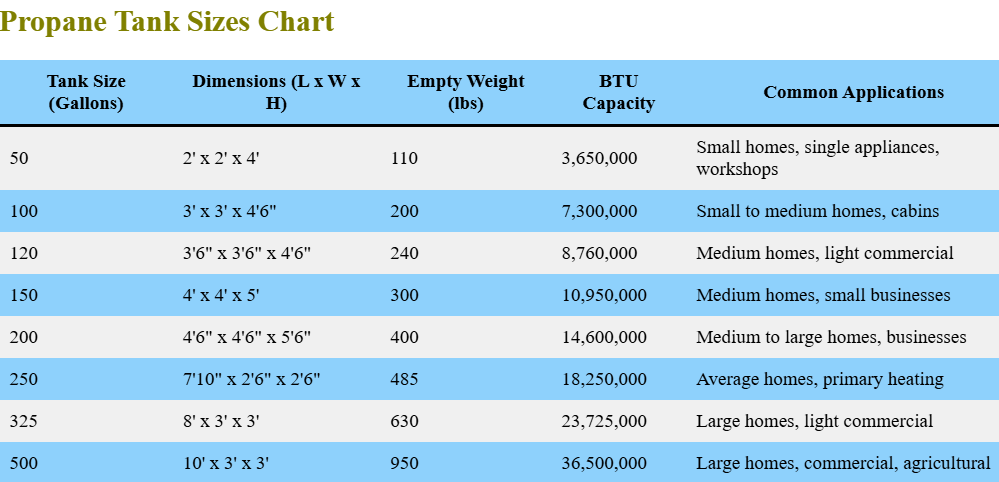
Propane Tank Sizes Chart
| Tank Size (Gallons) | Dimensions (L x W x H) | Empty Weight (lbs) | BTU Capacity | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 2′ x 2′ x 4′ | 110 | 3,650,000 | Small homes, single appliances, workshops |
| 100 | 3′ x 3′ x 4’6″ | 200 | 7,300,000 | Small to medium homes, cabins |
| 120 | 3’6″ x 3’6″ x 4’6″ | 240 | 8,760,000 | Medium homes, light commercial |
| 150 | 4′ x 4′ x 5′ | 300 | 10,950,000 | Medium homes, small businesses |
| 200 | 4’6″ x 4’6″ x 5’6″ | 400 | 14,600,000 | Medium to large homes, businesses |
| 250 | 7’10” x 2’6″ x 2’6″ | 485 | 18,250,000 | Average homes, primary heating |
| 325 | 8′ x 3′ x 3′ | 630 | 23,725,000 | Large homes, light commercial |
| 500 | 10′ x 3′ x 3′ | 950 | 36,500,000 | Large homes, commercial, agricultural |
Common Residential Propane Tank Sizes
120-Gallon Propane Tank
The 120-gallon tank represents an excellent entry point for homes with modest propane needs. Standing 54.5 inches tall and 30 inches in diameter, this vertical tank holds 96 gallons of propane when filled to capacity. It’s perfectly suited for homes running 1-2 propane appliances, such as:
- Water heaters
- Fireplaces
- Space heaters
- Ranges or clothes dryers (as supplemental appliances)
This size works well for smaller homes or as a secondary system in properties using multiple energy sources. Its compact footprint makes it ideal for properties with limited outdoor space.
250-Gallon Propane Tank
The 250-gallon horizontal tank measures 7 feet 10 inches long and 30 inches in diameter, holding 200 gallons of propane. This versatile size bridges the gap between small residential tanks and larger commercial systems. It comfortably supports:
- Clothes dryers
- Fireplaces
- Cooking ranges
- Heating systems for modest-sized homes (1,500-2,000 sq ft)
This tank size is particularly popular in temperate climates where heating demands are moderate. It provides enough capacity to avoid frequent refills while remaining cost-effective for installation and propane purchases.
325-Gallon Propane Tank
At 10 feet long and 30 inches in diameter, the 325-gallon tank holds 260 gallons of propane. This size serves as an excellent compromise between the 250 and 500-gallon options, making it ideal for:
- Backup generators
- Smaller homes using less than 500 gallons annually
- Properties with 3-4 propane appliances
Its increased capacity reduces refill frequency compared to smaller tanks, providing greater convenience during peak usage periods. The 325-gallon size is particularly well-suited for homes in moderate climates that use propane as their primary heating source.
500-Gallon Propane Tank
The 500-gallon tank (9’11” long and 37.5″ in diameter) is the workhorse of residential propane systems, holding 400 gallons of propane. As the standard size for most households, it reliably powers:
- Central heating systems for homes up to 3,500 sq ft
- Multiple high-demand appliances simultaneously
- Small commercial projects and agricultural operations
This tank size provides excellent value for homes in colder climates or those with high propane consumption. Its capacity ensures fewer deliveries and better protection against price fluctuations between refills.
Larger Commercial Propane Tanks Sizes
While our focus remains on residential sizes, understanding larger commercial tanks provides context for scaling propane systems:
| Tank Size | Propane Capacity | Dimensions | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 Gallon | 800 gallons | 16’1.5″ L x 41″ dia. | Large homes, commercial heating |
| 1,990 Gallon | 1,592 gallons | 23’11” L x 46.5″ dia. | Commercial heating, fleet filling |
| 30,000 Gallon | 24,000 gallons | 70′ L x 10′ H | Bulk plants, community metering |
These larger tanks typically serve commercial operations, agricultural facilities, or large residential communities with centralized propane distribution systems.
Small Propane Tanks for Specialized Applications
RV Propane Tanks
Recreational vehicles use specialized tanks designed for mobility and space efficiency:
| Size | Propane Capacity | Dimensions | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 lb | 4.7 gallons | 18″ H x 12.5″ dia. | Small RVs, camping trailers |
| 30 lb | 7 gallons | 24″ H x 12.5″ dia. | Medium RVs, motorhomes |
| 33 lb | 8 gallons | 26.75″ H x 12.5″ dia. | Larger RVs, extended trips |
| 100 lb | 23 gallons | 48″ H x 14.7″ dia. | Full-time RV living |
These tanks power everything from refrigerators and water heaters to furnaces and cooking appliances in mobile settings.
Portable Grill Tanks
The familiar 20-pound grill tank (4.7-gallon capacity) measures 1’6″ tall and 1′ in diameter. This versatile size powers:
- Backyard barbecue grills
- Portable heaters
- Camping stoves
- Small patio heaters
Its compact size and standardized fittings make it the most widely available propane tank for consumer use.
Forklift Propane Tanks
Industrial applications require specialized tanks designed for durability and frequent handling:
| Size | Propane Capacity | Dimensions | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 33 lb | 7.9 gallons | 29″ H x 13″ dia. | Light-duty forklifts |
| 43 lb | 10.3 gallons | 33″ H x 12.5″ dia. | Heavy-duty forklifts |
These tanks power propane forklifts in warehouses, construction sites, and agricultural operations, offering cleaner emissions and consistent power compared to gasoline or diesel alternatives.
What are the regulations for propane tank placement?
Propane tank placement is regulated by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) in NFPA 58, the Liquefied Petroleum Gas Code. These regulations specify minimum distances from buildings, property lines, ignition sources, and other tanks. Local jurisdictions may have additional requirements.
Always consult with your propane supplier and local building department to ensure compliance with all applicable propane tank regulations.
How to Choose the Right Propane Tank Size
Selecting the appropriate propane tank size for your needs requires careful consideration of several factors:
Calculate Your BTU Requirements
The first step in determining the right tank size is calculating your total BTU requirements. BTU measures the amount of energy needed to heat one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. Here’s how to calculate your needs:
- List all propane appliances in your home or business
- Find the BTU rating for each appliance (usually listed on the appliance or in the manual)
- Add up the BTU ratings to get your total demand
- Consider which appliances might run simultaneously (this is your peak demand)
For example:
- Furnace: 120,000 BTU/hour
- Water heater: 40,000 BTU/hour
- Range: 65,000 BTU/hour
- Dryer: 35,000 BTU/hour
Total BTU demand: 260,000 BTU/hour
Consider Your Usage Patterns
How you use propane significantly impacts the tank size you’ll need:
- Primary heating vs. supplemental heating
- Seasonal vs. year-round use
- Number of household members or employees
- Frequency of appliance use
Climate Considerations
Your local climate plays a crucial role in tank size selection:
- Colder climates require larger tanks due to longer heating seasons
- Areas with harsh winters may need additional capacity for extended periods between refills
- Remote locations might benefit from larger tanks to ensure adequate supply during weather-related delivery delays
Space and Installation Constraints
The physical space available for tank installation is a practical consideration:
- Above-ground tanks require specific clearances from buildings, property lines, and ignition sources
- Underground tanks need adequate space for excavation and future access
- Local zoning regulations and HOA restrictions may limit placement options
Budget Considerations
Your budget will influence your tank size decision:
- Larger tanks cost more initially but may save money in the long run through bulk purchasing and reduced delivery fees
- Installation costs vary between above-ground and underground options
- Some propane suppliers offer tank leasing options that reduce upfront costs
Installation Requirements for Different Tank Sizes
Proper propane tank installation is essential for safety and efficiency. Installation requirements vary based on tank size and whether it’s installed above ground or underground.
Above-Ground Installation Requirements
Placement Clearances
All above-ground propane tanks must maintain specific distances from buildings, property lines, and potential ignition sources:
| Tank Size | Minimum Distance from Building | Minimum Distance from Property Line | Minimum Distance from Ignition Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50-125 gallons | 10 feet | 5 feet | 10 feet |
| 126-250 gallons | 10 feet | 5 feet | 10 feet |
| 251-500 gallons | 10 feet | 10 feet | 10 feet |
Foundation Requirements
Above-ground tanks require a stable, level foundation:
- Concrete pads are the preferred foundation material
- The foundation must extend at least 6 inches beyond the tank footprint
- The area should be graded to prevent water accumulation under the tank
- Tanks over 125 gallons require anchoring to prevent movement
Underground Installation Requirements
Placement Considerations
Underground propane tanks offer aesthetic advantages but have specific requirements:
- Must be installed in well-drained soil to prevent corrosion
- Require specific clearances from wells, septic systems, and underground utilities
- Need protective coating and cathodic protection to prevent corrosion
- Must be accessible for future maintenance and inspections
Excavation Requirements
Proper excavation is crucial for underground tank installation:
- The excavation hole must be large enough to accommodate the tank and protective backfill
- A minimum of 6 inches of sand or fine gravel must be placed beneath the tank
- The tank should be covered with at least 12 inches of earth
- Warning tape must be placed above the tank to alert future excavators
Propane Tank Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when dealing with propane storage. Here are essential propane tank safety considerations for propane tanks of all sizes:
Regular Inspections
Propane tanks should be inspected regularly:
- Visual inspections should be performed monthly by the user
- Professional inspections should be conducted annually
- Look for signs of rust, damage, or leaks
- Ensure valves and gauges are functioning properly
Proper Ventilation
Propane tanks require adequate ventilation:
- Never store tanks in enclosed spaces
- Ensure tank areas are free from debris and vegetation
- Maintain proper clearances as specified by local codes
Leak Detection
Knowing how to detect propane leaks is crucial:
- Propane has a distinctive rotten egg smell (odorant is added for detection)
- Listen for hissing sounds near the tank or lines
- Use soapy water to check for bubbles at connection points
- Install propane gas detectors in your home or business
Emergency Procedures
Know what to do in case of an emergency:
- If you smell gas, evacuate the area immediately
- Do not operate electrical switches or use phones in the area
- Call your propane supplier or emergency services from a safe location
- Do not attempt to fix the problem yourself
Maintenance Tips for Propane Tanks
Proper propane tank maintenance extends the life of your propane tank and ensures safe operation:
Seasonal Maintenance
Different seasons require different maintenance tasks:
- Before winter: Ensure adequate propane levels, check for snow load risks
- During winter: Keep tank clear of snow and ice, ensure vents remain unobstructed
- Spring: Inspect for winter damage, check regulator and fittings
- Summer: Ensure vegetation is cleared around the tank, check for insect nests in vents
Long-Term Maintenance
For the long-term health of your propane tank:
- Keep the tank painted to prevent rust (use light, reflective colors)
- Ensure tank supports remain stable and level
- Protect gauges and valves from damage
- Schedule professional maintenance as recommended by your supplier
Tank Lifespan and Replacement
Propane tanks have a finite propane tank lifespan:
- Most propane tanks are certified for 12 years initially
- After 12 years, they must be recertified or replaced
- Tanks showing significant rust or damage should be replaced immediately
- Underground tanks typically last 20-30 years with proper maintenance
FAQs
How long will a 500-gallon propane tank last for heating?
The lifespan of a 500-gallon propane tank depends on several factors including home size, climate, and heating efficiency. On average, a 500-gallon tank can last anywhere from 2-6 months during the heating season. In a cold climate with a large home, it might last only 2-3 months, while in a moderate climate with an efficient heating system, it could last 5-6 months or longer.
Can I install a propane tank myself?
No, propane tank installation should always be performed by trained professionals. Licensed propane technicians have the expertise to properly install tanks, connect lines, test for leaks, and ensure compliance with all local codes and safety regulations. DIY installation can result in dangerous leaks, improper placement, and code violations that could void your insurance.
How far does a propane tank need to be from the house?
The required distance between a propane tank and a house depends on the tank size and local codes. For tanks between 50-500 gallons, the minimum distance is typically 20 feet from buildings. However, local regulations may require greater distances, so it’s essential to check with your local building department and propane supplier for specific requirements in your area.
How often do propane tanks need to be replaced?
Propane tanks have specific certification periods. Most new tanks are certified for 12 years. After this period, they must be recertified or replaced. Recertification can extend the tank’s life for an additional 5, 7, or 12 years depending on the method used. However, tanks showing significant rust, damage, or other safety concerns should be replaced immediately regardless of certification status.
Can propane tanks be buried underground?
Yes, propane tanks can be installed underground. Underground installations offer aesthetic advantages by hiding the tank from view. However, they require special corrosion protection, proper excavation, and specific placement considerations. Underground tanks typically cost more to install but may be preferred in areas with strict appearance regulations or where space is limited.
Final Thoughts:
Choosing the right propane tank size is crucial for ensuring a reliable supply of propane for your home or business. Whether you need a 50-gallon tank for a small cabin or a 500-gallon tank for a large home with multiple appliances, understanding the options and requirements will help you make an informed decision.
Remember to consider your BTU requirements, usage patterns, climate conditions, and installation constraints when selecting a tank size. Always work with licensed professionals for installation and maintenance to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
By carefully selecting and maintaining your propane tank, you’ll enjoy the many benefits of propane as a clean, efficient, and versatile energy source for years to come.
Affiliate Disclosure: Fireplaceadviser.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program. We may earn a commission when you click on certain links on this site and purchase.

Hello!! I am Jamal Khan. I often fix my home electric heaters and gas stove problems and research the common issues in the heating units to improve my knowledge and expertise. The aim of establishing fireplaceadviser.com is to share my expertise and knowledge with my audience.


















