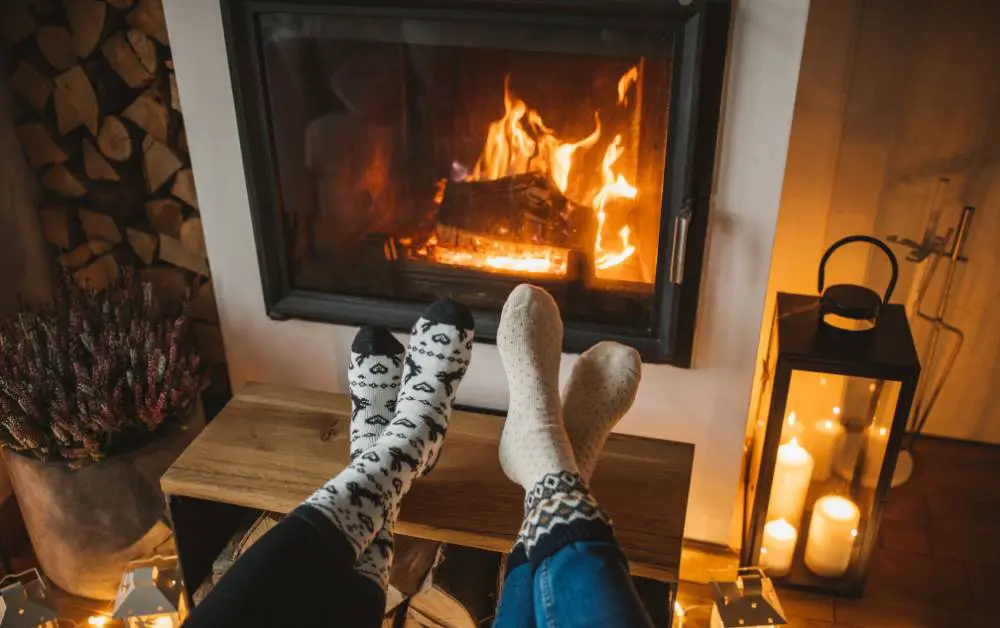
The mesmerizing dance of flames has long captivated our attention, not only for its aesthetic beauty but also for the valuable insights it offers into the science of combustion.
Understanding the colors of a flame goes beyond mere visual appreciation; it unveils a spectrum of temperatures and the fascinating chemistry at play within the heart of the fire.
In this exploration of the “Flame Color Temperature Chart,” we embark on a journey to decipher the language of fire, unraveling the secrets behind each hue and the temperatures they signify.
Flame Color Temperature Chart
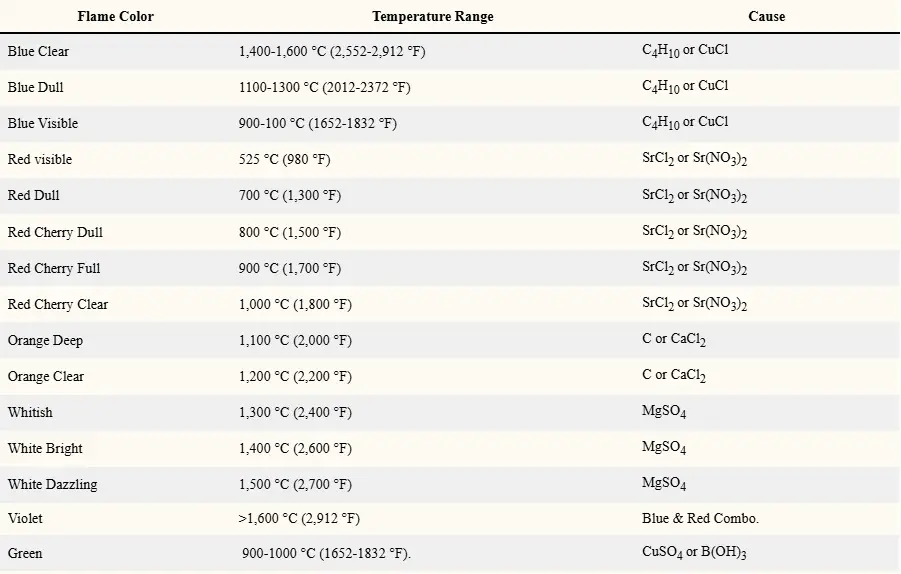
| Flame Color | Temperature Range | Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Blue Clear | 1,400-1,600 °C (2,552-2,912 °F) | C4H10 or CuCl |
| Blue Dull | 1100-1300 °C (2012-2372 °F) | C4H10 or CuCl |
| Blue Visible | 900-100 °C (1652-1832 °F) | C4H10 or CuCl |
| Red visible | 525 °C (980 °F) | SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2 |
| Red Dull | 700 °C (1,300 °F) | SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2 |
| Red Cherry Dull | 800 °C (1,500 °F) | SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2 |
| Red Cherry Full | 900 °C (1,700 °F) | SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2 |
| Red Cherry Clear | 1,000 °C (1,800 °F) | SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2 |
| Orange Deep | 1,100 °C (2,000 °F) | C or CaCl2 |
| Orange Clear | 1,200 °C (2,200 °F) | C or CaCl2 |
| Whitish | 1,300 °C (2,400 °F) | MgSO4 |
| White Bright | 1,400 °C (2,600 °F) | MgSO4 |
| White Dazzling | 1,500 °C (2,700 °F) | MgSO4 |
| Violet | >1,600 °C (2,912 °F) | Blue & Red Combo. |
| Green | 900-1000 °C (1652-1832 °F). | CuSO4 or B(OH)3 |
| Yellow | 1148 °C (2100 °F) | Fe or Na |
| Purple | 982 °C (1800 °F) | Blue & Red Combo. |
Flame Colors Characteristics
- Blue Clear:
- Temperature Range: 1,400-1,600 °C (2,552-2,912 °F)
- Cause: Presence of C4H10 or CuCl
- Characteristics: Intense, clear blue flame indicative of high-temperature combustion with the presence of specific organic compounds or copper chloride.
- Blue Dull:
- Temperature Range: 1,100-1,300 °C (2012-2372 °F)
- Cause: Presence of C4H10 or CuCl
- Characteristics: Subdued blue flame suggesting a slightly lower temperature compared to clear blue; likely due to the same organic compounds or copper chloride.
- Blue Visible:
- Temperature Range: 900-1,000 °C (1652-1832 °F)
- Cause: Presence of C4H10 or CuCl
- Characteristics: Faint blue flame visible at lower temperatures, demonstrating the sensitivity of flame color to temperature changes with the same organic compounds or copper chloride.
- Red Visible:
- Temperature: 525 °C (980 °F)
- Cause: Presence of SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2
- Characteristics: Gentle red flame visible at a relatively lower temperature, usually associated with the combustion of strontium compounds.
- Red Dull:
- Temperature: 700 °C (1,300 °F)
- Cause: Presence of SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2
- Characteristics: Dimmer red flame suggesting a moderate temperature, often linked to the burning of strontium compounds.
- Red Cherry Dull:
- Temperature: 800 °C (1,500 °F)
- Cause: Presence of SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2
- Characteristics: Warm, cherry-red flame with a dull glow, reflecting a higher combustion temperature of strontium compounds.
- Red Cherry Full:
- Temperature: 900 °C (1,700 °F)
- Cause: Presence of SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2
- Characteristics: Full-bodied cherry-red flame, indicating an even higher combustion temperature of strontium compounds.
- Red Cherry Clear:
- Temperature: 1,000 °C (1,800 °F)
- Cause: Presence of SrCl2 or Sr(NO3)2
- Characteristics: Clear and vibrant cherry-red flame, suggesting an elevated temperature during the combustion of strontium compounds.
- Orange Deep:
- Temperature: 1,100 °C (2,000 °F)
- Cause: Presence of C or CaCl2
- Characteristics: Deep orange flame, indicative of high-temperature combustion with the presence of carbon or calcium chloride.
- Orange Clear:
- Temperature: 1,200 °C (2,200 °F)
- Cause: Presence of C or CaCl2
- Characteristics: Clear and bright orange flame, signifying a slightly higher combustion temperature with carbon or calcium chloride.
- Whitish:
- Temperature: 1,300 °C (2,400 °F)
- Cause: Presence of MgSO4
- Characteristics: Soft whitish flame, demonstrating high-temperature combustion with the presence of magnesium sulfate.
- White Bright:
- Temperature: 1,400 °C (2,600 °F)
- Cause: Presence of MgSO4
- Characteristics: Intensely bright white flame, indicative of a very high combustion temperature with magnesium sulfate.
- White Dazzling:
- Temperature: 1,500 °C (2,700 °F)
- Cause: Presence of MgSO4
- Characteristics: Dazzling white flame, reflecting an exceptionally high combustion temperature with magnesium sulfate.
- Violet:
- Temperature: >1,600 °C (2,912 °F)
- Cause: Blue & Red Combo.
- Characteristics: Violet flame resulting from a combination of blue and red flames, showcasing a very high combustion temperature.
- Green:
- Temperature Range: 900-1,000 °C (1652-1832 °F)
- Cause: Presence of CuSO4 or B(OH)3
- Characteristics: Green flame indicative of the presence of copper sulfate or boric acid, demonstrating a moderate combustion temperature.
- Yellow:
- Temperature: 1,148 °C (2,100 °F)
- Cause: Presence of Fe or Na
- Characteristics: Yellow flame resulting from the combustion of iron or sodium compounds, showcasing a moderate combustion temperature.
- Purple:
- Temperature: 982 °C (1,800 °F)
- Cause: Blue & Red Combo.
- Characteristics: Purple flame resulting from a combination of blue and red flames, indicative of a moderate combustion temperature.
Flame Color Temperature Chart Infographic

FAQs
What is the hottest fire color?
How hot is blue fire?
Blue flames burn at approximately 1,400 to 1,650 degrees Celsius (2,552 to 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit), indicating efficient combustion with a high oxygen supply
How hot is green fire?
How hot is purple fire?
How hot is white flames?
Related Posts:
Affiliate Disclosure: Fireplaceadviser.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program. We may earn a commission when you click on certain links on this site and purchase.

Hello!! I am Jamal Khan. I often fix my home electric heaters and gas stove problems and research the common issues in the heating units to improve my knowledge and expertise. The aim of establishing fireplaceadviser.com is to share my expertise and knowledge with my audience.









