Propane contains approximately 91,500 BTUs per gallon, making it one of the most efficient and versatile fuel sources available for residential and commercial use. This high energy density means propane can deliver substantial heat output while requiring less storage space than many alternative fuels.
Understanding the BTU content of propane is essential for calculating energy costs, comparing fuel efficiency, and determining the right size propane tank for your needs.
Key Takeaways
- A gallon of propane contains approximately 91,500 BTUs of energy
- Propane has a higher BTU rating than many other common fuels, including natural gas and electricity
- The exact BTU content can vary slightly based on propane quality and ambient conditions
- Understanding propane’s BTU rating helps with calculating appliance runtime and heating costs
- Propane’s high energy density makes it efficient for various applications from home heating to industrial uses
What is BTU and Why It Matters for Propane
A British Thermal Unit (BTU) is the standard measurement used to quantify heat energy. Specifically, one BTU represents the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. While this might sound technical, understanding BTUs is crucial when working with propane and other fuels because it allows for direct comparisons of energy content.
When we talk about propane energy content, we’re referring to how much usable heat energy can be extracted from a given amount of propane. This measurement helps consumers and professionals alike determine how efficiently propane can power appliances, heat spaces, and fuel equipment.
For homeowners, BTU ratings are particularly important when sizing heating systems, estimating fuel costs, and comparing different energy sources. The higher the BTU rating per unit of fuel, the more heat energy that fuel can provide, which typically translates to better efficiency and lower operating costs.
BTU Per Gallon of Propane
When we discuss the BTU per gallon of propane, we’re looking at one of the most significant advantages of propane as a fuel source. A standard US gallon of propane contains approximately 91,500 BTUs of heat energy. This high energy density is one of the primary reasons propane is so popular for a wide range of applications.
To put this in perspective, this means that a relatively small amount of propane can generate a substantial amount of heat. For example, a typical 20-pound propane grill tank (which holds about 4.7 gallons of propane) contains approximately 430,000 BTUs of energy—enough to fuel a medium-sized grill for about 18-20 hours of cooking time.
It’s worth noting that the exact BTU content can vary slightly based on several factors:
- Propane Quality: The purity of propane can affect its BTU content. Commercial propane typically contains at least 90% propane, with the remainder being other gases like butane and methane.
- Temperature: Propane’s energy density is affected by temperature. Colder temperatures can slightly reduce the BTU content per gallon.
- Measurement Standards: The industry standard for measuring propane BTU is based on liquid propane at 60°F. Variations from this temperature can result in slight differences in BTU content.
Despite these minor variables, the 91,500 BTU per gallon figure is widely accepted as the standard for calculations and comparisons in the industry.
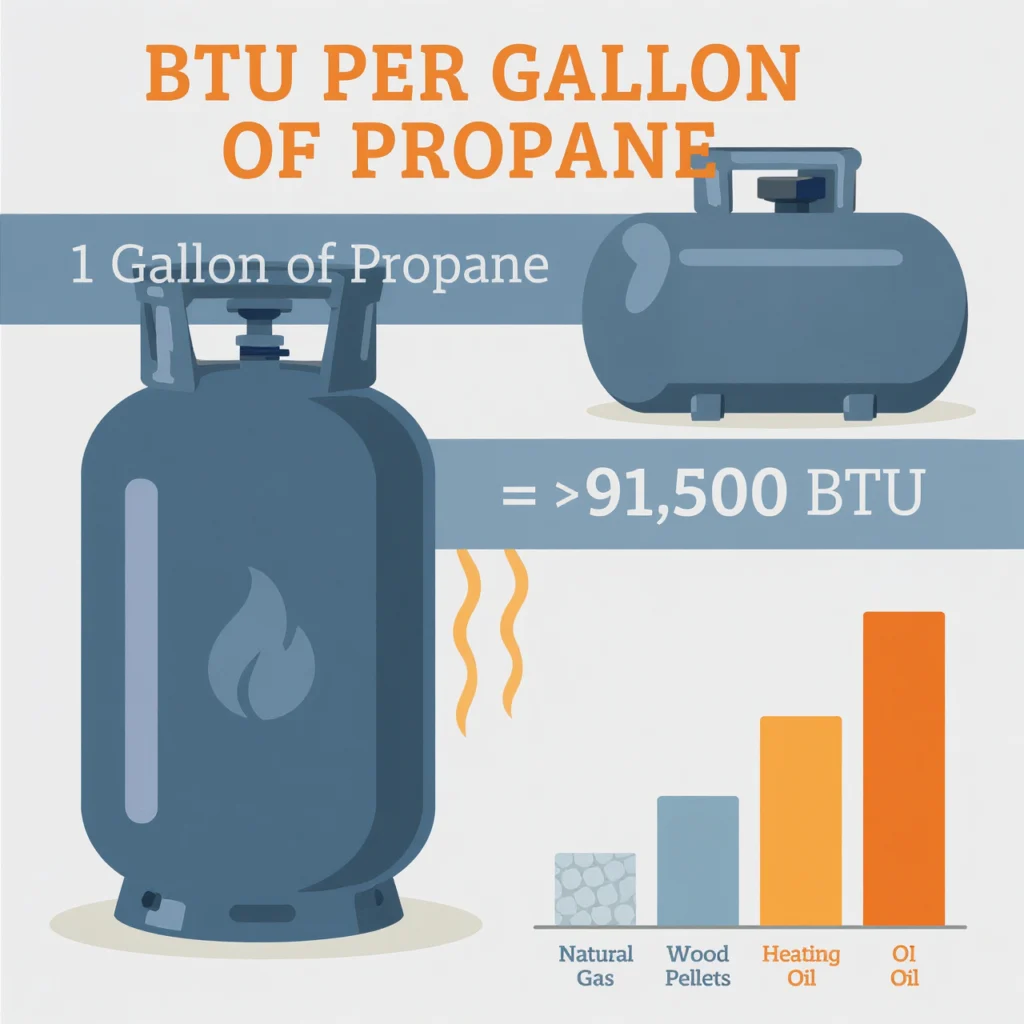
How Propane Compares to Other Fuels (BTU Comparison)
Understanding how propane stacks up against other fuel sources is essential for making informed energy decisions. Let’s compare the BTU content of propane with other common fuels:
| Fuel Type | BTU per Unit | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Propane | 91,500 | Gallon |
| Gasoline | 124,000 | Gallon |
| Diesel Fuel | 139,000 | Gallon |
| Natural Gas | 1,030 | Cubic Foot |
| Electricity | 3,413 | Kilowatt Hour |
| Heating Oil | 138,500 | Gallon |
| Wood (Oak) | 26,000,000 | Cord |
| Coal (Anthracite) | 25,000,000 | Ton |
When comparing these fuels, it’s important to consider not just the BTU content but also the cost per BTU, efficiency of the appliances using the fuel, and other practical considerations like storage and availability.
For example, while heating oil has a higher BTU per gallon than propane, propane appliances are typically more efficient, often resulting in lower overall heating costs. Similarly, while natural gas has a lower BTU per cubic foot than propane per gallon, natural gas is often less expensive per BTU in areas where it’s available.
The propane vs other fuels comparison becomes particularly interesting when considering environmental impact, convenience, and appliance efficiency—all factors that we’ll explore in later sections.
Factors Affecting Propane’s BTU Output
While 91,500 BTUs per gallon is the standard measurement for propane, several factors can influence the actual BTU output you experience in real-world applications:
1. Propane Purity
Commercial propane isn’t 100% pure propane. It typically contains small amounts of other hydrocarbons, primarily butane. The exact composition can vary by season and region, with winter blends often containing more propane (which performs better in cold weather) and summer blends containing more butane.
The propane energy density is highest when the propane is most pure. Most commercial propane sold in the United States contains at least 90% propane, with the remaining 10% consisting primarily of other gases.
2. Temperature Effects
Propane’s BTU content is measured at a standard temperature of 60°F. As temperatures drop, propane contracts, meaning you get slightly less energy per gallon. Conversely, in warmer temperatures, propane expands, providing slightly more energy per gallon.
This temperature effect is relatively minor for most residential applications but can be significant for large commercial or industrial users who measure propane consumption precisely.
3. Appliance Efficiency
The BTU rating of propane measures the total energy content, but not all of this energy is converted to useful heat in your appliances. The efficiency of your propane furnace, water heater, or other equipment determines how much of the available energy is actually used for its intended purpose.
Modern propane appliances typically have efficiency ratings between 80% and 98%, meaning they convert 80-98% of the propane’s BTU content into usable heat. The rest is lost through exhaust gases and other inefficiencies.
4. Altitude
At higher altitudes, propane contains slightly less energy per gallon due to changes in atmospheric pressure. This effect is generally minimal but can be noticeable in mountainous regions above 5,000 feet.
5. Storage and Handling
Propane must be stored and handled properly to maintain its energy content. Exposure to contaminants, improper storage conditions, or aging of the propane can all potentially affect its BTU output, though these factors are generally well-controlled in the commercial propane supply chain.
Calculating Your Propane Needs Based on BTU
Understanding the BTU content of propane is only useful if you can apply it to your specific needs. Here’s how to calculate your propane requirements:
Step 1: Determine Your BTU Requirements
First, identify the BTU requirements of your appliances. This information is typically found on the appliance’s nameplate or in the owner’s manual. For example:
- A typical propane furnace might use 100,000 BTUs per hour
- A propane water heater might use 40,000 BTUs per hour
- A propane range might use 25,000 BTUs per hour for all burners combined
- A propane clothes dryer might use 22,000 BTUs per hour
Step 2: Estimate Daily Usage
Next, estimate how many hours per day each appliance will run:
- Furnace: Perhaps 10 hours per day in cold weather
- Water heater: Maybe 3 hours per day
- Range: Approximately 1 hour per day
- Clothes dryer: About 0.5 hours per day
Step 3: Calculate Daily BTU Consumption
Multiply each appliance’s BTU rating by its daily runtime:
- Furnace: 100,000 BTU/hour × 10 hours = 1,000,000 BTUs per day
- Water heater: 40,000 BTU/hour × 3 hours = 120,000 BTUs per day
- Range: 25,000 BTU/hour × 1 hour = 25,000 BTUs per day
- Clothes dryer: 22,000 BTU/hour × 0.5 hours = 11,000 BTUs per day
Total daily BTU consumption: 1,156,000 BTUs
Step 4: Convert to Gallons of Propane
Divide the total daily BTU consumption by the BTU content per gallon of propane (91,500 BTUs/gallon):
1,156,000 BTUs ÷ 91,500 BTUs/gallon = 12.6 gallons of propane per day
Step 5: Project Your Needs
Multiply your daily consumption by the number of days between propane deliveries or tank refills to determine your storage needs:
12.6 gallons/day × 30 days = 378 gallons per month
This calculation helps you determine the appropriate size propane tank for your needs and estimate your fuel costs. For a more precise calculation, you can use a propane BTU calculator available online or consult with a propane supplier.
Maximizing Propane Efficiency in Your Home
Given that propane contains approximately 91,500 BTUs per gallon, maximizing the efficiency of your propane appliances can lead to significant cost savings. Here are some strategies to get the most out of every gallon:
1. Upgrade to High-Efficiency Appliances
Modern propane appliances are significantly more efficient than older models. For example:
- Propane furnaces: New models can achieve efficiency ratings of up to 98%, compared to 80-85% for older models
- Propane water heaters: Tankless models can achieve efficiency ratings above 90%, while traditional tank models typically range from 70-85%
- Propane clothes dryers: New models use 15-20% less energy than those from a decade ago
Upgrading to high-efficiency appliances can reduce your propane consumption by 15-30% or more, depending on the age and efficiency of your current equipment.
2. Regular Maintenance
Keeping your propane appliances well-maintained ensures they operate at peak efficiency:
- Clean or replace furnace filters monthly during heating season
- Have your propane furnace professionally serviced annually
- Drain your water heater tank annually to remove sediment
- Clean dryer vents and lint traps regularly
- Check for leaks in your propane system periodically
Proper maintenance not only improves efficiency but also extends the life of your appliances and enhances safety.
3. Home Insulation and Weatherization
No matter how efficient your propane appliances are, they’ll work harder and use more fuel if your home isn’t properly insulated and sealed:
- Add insulation to attics, walls, and basements
- Seal air leaks around windows, doors, and electrical outlets
- Install storm windows or replace old single-pane windows with energy-efficient models
- Add weatherstripping to doors and windows
- Insulate hot water pipes and the water heater tank
These improvements can reduce your heating needs by 20-30%, directly translating to lower propane consumption.
4. Smart Thermostats and Controls
Installing smart thermostats and controls can optimize your propane usage:
- Programmable thermostats can reduce heating when you’re away or asleep
- Smart water heater controllers can optimize water heating based on your usage patterns
- Remote monitoring systems can help you track your propane usage and detect potential issues
These technologies typically pay for themselves through energy savings within 1-2 years.
5. Consider Zoned Heating
If you have a larger home, zoned heating systems can direct heat only to the areas being used, rather than heating the entire house to the same temperature. This approach can reduce your heating fuel consumption by 10-20% while maintaining comfort in the spaces you’re using.
Propane BTU Applications
The high BTU content of propane—91,500 BTUs per gallon—makes it suitable for a wide range of applications across residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural sectors. Let’s explore some of the most common uses:
Residential Applications
- Home Heating: Propane furnaces and boilers provide efficient, consistent heat for homes. A typical residential propane furnace might have a BTU input rating between 60,000 and 120,000 BTUs per hour.
- Water Heating: Propane water heaters, both tank and tankless models, offer faster recovery times and lower operating costs than electric models. A typical residential propane water heater might have an input rating of 30,000 to 50,000 BTUs per hour.
- Cooking: Professional chefs and home cooks alike prefer propane ranges for their precise temperature control and instant heat. A typical propane range burner might output 7,000 to 15,000 BTUs per hour, with high-power burners reaching up to 20,000 BTUs per hour.
- Clothes Drying: Propane dryers dry clothes faster and more efficiently than electric models. A typical propane clothes dryer uses approximately 22,000 BTUs per hour.
- Fireplaces and Inserts: Propane fireplaces provide the ambiance of a wood fire without the mess and with greater efficiency. These typically output between 20,000 and 40,000 BTUs per hour.
- Backup Generators: Propane-powered generators provide reliable backup power during outages. Residential models might consume between 1-3 gallons of propane per hour, depending on the electrical load.
Commercial Applications
- Space Heating: Commercial buildings often use propane furnaces or boilers for heating. These systems can have input ratings from 100,000 to several million BTUs per hour.
- Water Heating: Restaurants, hotels, and laundromats rely on high-capacity propane water heaters. Commercial systems might have input ratings from 100,000 to 1,000,000 BTUs per hour.
- Cooking: Commercial kitchens use propane for ranges, ovens, fryers, and grills. A commercial propane range might have burners rated at 15,000 to 35,000 BTUs per hour.
- Forklifts: Propane-powered forklifts are popular in warehouses and distribution centers due to their consistent power and clean operation. A typical forklift might consume 1-2 gallons of propane per hour of operation.
Industrial Applications
- Process Heating: Manufacturing facilities use propane for various heating processes, with systems rated from hundreds of thousands to millions of BTUs per hour.
- Metal Fabrication: Propane is used for cutting, brazing, soldering, and heat treating metals. Propane torches might output 50,000 to 200,000 BTUs per hour.
- Agriculture: Farmers use propane for crop drying, space heating in poultry and livestock operations, and irrigation pumps. Crop dryers might consume several gallons of propane per hour.
- Construction: Temporary heating during construction is often provided by propane heaters, with models ranging from small 30,000 BTU units to large construction heaters rated at over 1,000,000 BTUs per hour.
You May Also Like:
FAQs
How many BTUs are in a gallon of propane?
A standard US gallon of propane contains approximately 91,500 BTUs of heat energy. This is the industry standard measurement used for calculations and comparisons.
How does the BTU
Propane contains about 2.5 times more energy per unit than natural gas. A gallon of propane (91,500 BTUs) is roughly equivalent to 91 cubic feet of natural gas (which contains about 1,030 BTUs per cubic foot).
Does the BTU content of propane vary by season?
The BTU content of propane can vary slightly by season due to different blends. Winter blends typically contain more propane, which has a higher BTU content than butane (which is more common in summer blends). However, these variations are typically minor and don’t significantly affect appliance performance.
How long will a 20-pound propane tank last?
A standard 20-pound propane grill tank contains about 4.7 gallons of propane, which equals approximately 430,000 BTUs of energy. How long it lasts depends on your grill’s BTU rating. For example, if your grill uses 30,000 BTUs per hour, the tank would last about 14 hours of continuous use.
Affiliate Disclosure: Fireplaceadviser.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program. We may earn a commission when you click on certain links on this site and purchase.

Hello!! I am Jamal Khan. I often fix my home electric heaters and gas stove problems and research the common issues in the heating units to improve my knowledge and expertise. The aim of establishing fireplaceadviser.com is to share my expertise and knowledge with my audience.












